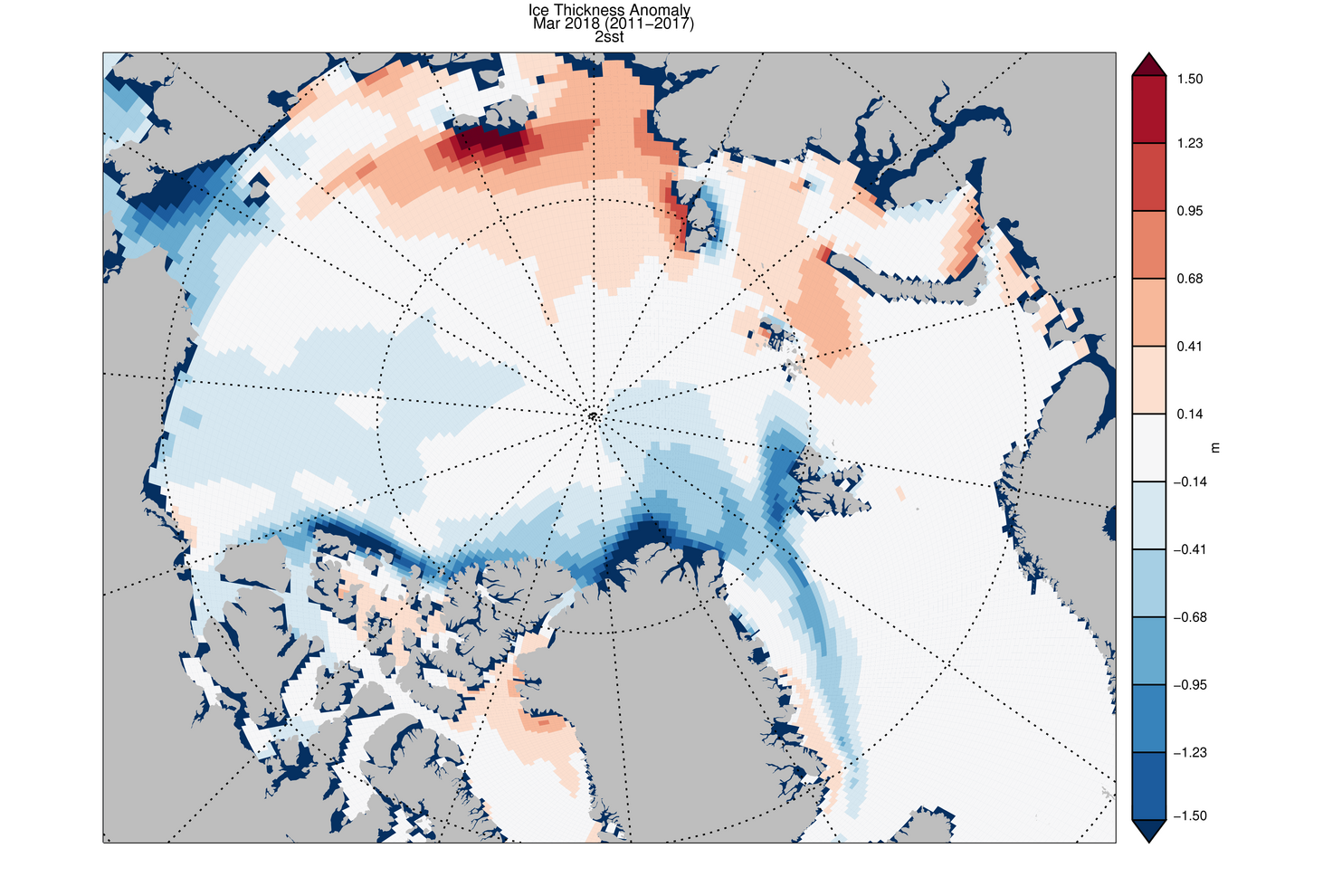
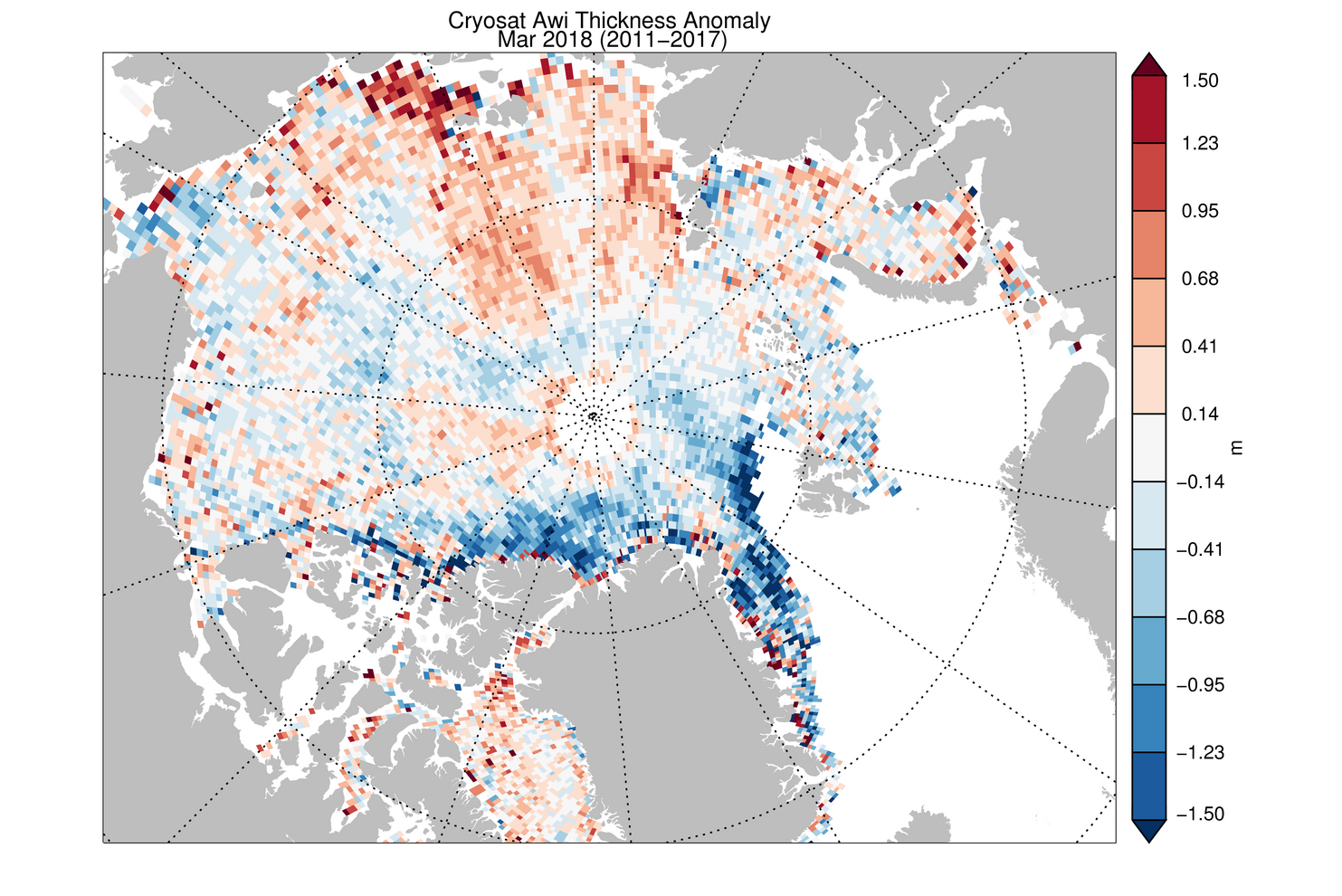
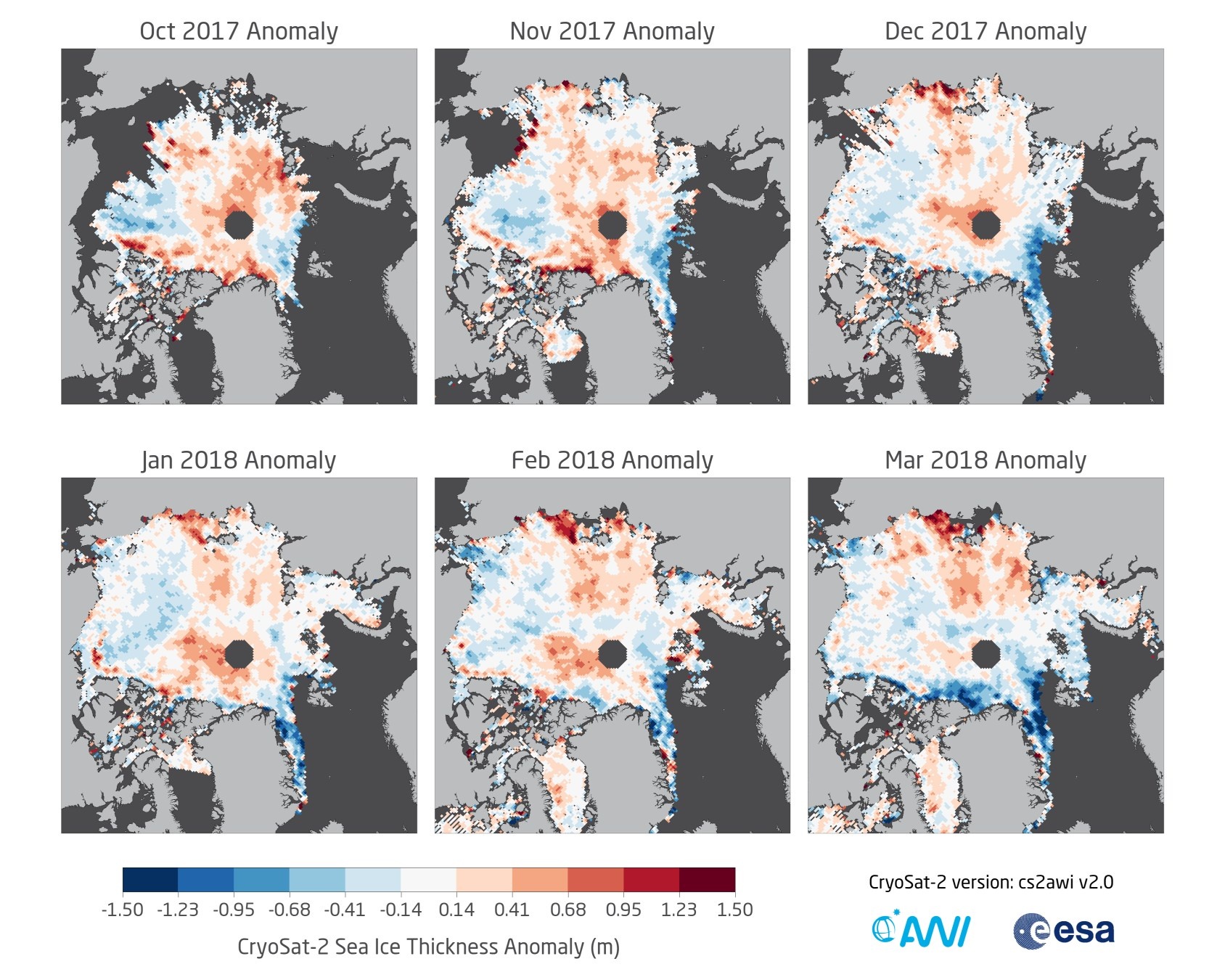
One useful method to evaluate sea ice thickness information from remote sensing and numerical models is to compare monthly anomalies. This parameter is defined as the difference of one particular month to the mean monthly thickness fields of other month in the data record. Monthly anomalies are therefore sensitive to processes that cause sea ice thickness changes and can be compared to other sources which may have a systematic thickness bias to the reference thickness field.
One of these comparisons is regularly carried by the Polar Science Center (PSC) of the Applied Physics Laboratory at the University of Washington. The PSC operates the Pan-Arctic Ice Ocean Modeling and Assimilation System (PIOMAS) that provides near-real time updates of Arctic sea ice thickness and volume.
PIOMAS March 2018 sea ice thickness anomaly
(credit: Axel Schweiger, Polar Science Center, Source)
CryoSat-2 March 2018 sea ice thickness anomaly projected to PIOMAS grid
(credit: Axel Schweiger, Polar Science Center, Source)